Ad Code
Categories
About Me
Translate
Advertising
Total Pageviews
Recent Posts
{getWidget} $results={4} $label={recent}

Random Posts
randomposts
Advertisement
Subscribe Us
Popular Posts

CISCO CCNA SWITCHING
1:48:00 AM

STP ( Spanning tree protocol )
1:48:00 AM
What is BPDU & ROOT GUARD
BPDU Guard
BPDU stands for bridge protocol data unit. BPDUs are data messages that are exchanged across the switches within an extended LAN that uses a spanning tree protocol topology. BPDU packets contain information on ports, addresses, priorities and costs and ensure that the data ends up where it was intended to go. BPDU messages are exchanged across bridges to detect loops in a network topology. The loops are then removed by shutting down selected bridge interfaces and placing redundant switch ports in a backup, or blocked, state.
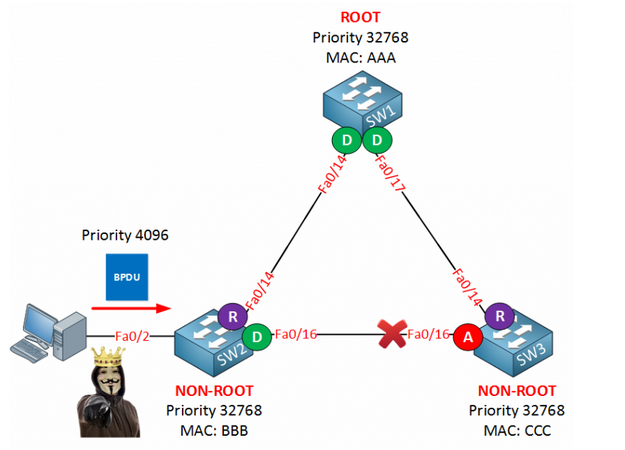
BPDU Guard: Prevents accidental connection of switching
devices to PortFast-enabled ports. Connecting switches to
PortFast-enabled ports can cause Layer 2 loops or topology changes.
Root Guard
Root Guard is useful in avoiding Layer 2 loops during network anomalies. The Root Guard feature forces an interface to become a designated port to prevent surrounding switches from becoming a root switch. In other words, Root Guard provides a way to enforce the root bridge placement in the network. The Root Guard feature prevents a Designated Port from becoming a Root Port. If a port on which the Root Guard feature receives a superior BPDU, it moves the port into a root-inconsistent state (effectively equal to a listening state), thus maintaining the current Root Bridge status.
BPDU stands for bridge protocol data unit. BPDUs are data messages that are exchanged across the switches within an extended LAN that uses a spanning tree protocol topology. BPDU packets contain information on ports, addresses, priorities and costs and ensure that the data ends up where it was intended to go. BPDU messages are exchanged across bridges to detect loops in a network topology. The loops are then removed by shutting down selected bridge interfaces and placing redundant switch ports in a backup, or blocked, state.

Root Guard
Root Guard is useful in avoiding Layer 2 loops during network anomalies. The Root Guard feature forces an interface to become a designated port to prevent surrounding switches from becoming a root switch. In other words, Root Guard provides a way to enforce the root bridge placement in the network. The Root Guard feature prevents a Designated Port from becoming a Root Port. If a port on which the Root Guard feature receives a superior BPDU, it moves the port into a root-inconsistent state (effectively equal to a listening state), thus maintaining the current Root Bridge status.
Footer Menu Widget
Created By Blogspot Theme | Distributed By Gooyaabi Templates





Social Plugin